Hybrid Architecture in Collective Property and Facility Management: ACR Site Management System
Project: ACR Site Management System
Access URL: app-siteyonetim.acrtech.com.tr
Document Type: Technical Architecture Analysis and System Review
Abstract
ACR Site Management System is designed to manage the financial and administrative processes of collective living spaces such as apartments, complexes, and business centers.
The project combines the fluidity of a desktop application (Electron.js & React) in terms of user experience with enterprise backend architecture (Spring Boot & MongoDB) for data security and transaction integrity. It distinguishes itself from standard software specifically with "Storno" accounting principles, asynchronous mass debiting services, and a NoSQL-based dynamic reporting engine.
1. Introduction and Problem Space
Site managements are generally managed with Excel files or old-generation desktop software. This situation leads to the following problems:
- Data Inconsistency: When a flat's debt is deleted, the fate of the money in the cash box becomes unclear (Lack of Audit Trail).
- Performance Issues: In a complex with hundreds of flats, adding dues debt to everyone with a single click can lock up systems.
- Lack of Flexibility: Apart from fixed expenses, extraordinary expenses like "Roof Repair" cannot be instantly reflected to the flat owners.
ACR Site Management solves these problems with a modern "Event-Driven" and "Asynchronous" approach.
2. System Architecture and Technology Stack
The project is in a Client-Server architecture and uses a hybrid structure on the client side.
2.1. Backend (Server Layer)
The brain of the system is the RESTful API service running on Spring Boot 3.5.
- Database: MongoDB. In site management, the data schema (fixture properties, transaction types) can change over time. MongoDB's schemaless structure provides this flexibility.
- Data Integrity: Despite using NoSQL, the uniqueness of the "Block ID + Door No" combination is guaranteed at the database level using
@CompoundIndexin theFlatmodel. - Asynchronous Architecture: Long-running processes (e.g., accruing debt to 500 flats) are executed in the background without blocking the main thread using the
@Asyncannotation and Spring'sTaskExecutorstructure.
2.2. Frontend & Desktop (Client Layer)
The user interface is developed with React and Material UI (MUI), compiled with Vite, and packaged with Electron.
- Electron Integration: The interface developed with web technologies (HTML/CSS/JS) works like a native desktop application (Windows/macOS/Linux) thanks to Electron.
- CRUD Hook Architecture: The
useCrudApicustom hook developed on the frontend side manages all API requests, error handling, and loading states from a central point.
3. Critical Technical Features and Solutions
"Best Practice" applications standing out in the project's source codes:
3.1. Asynchronous Mass Debiting (Async Processing)
Adding dues debt to hundreds of flats at the same time is a costly operation.
- Problem: The browser freezing when the user clicks the "Debit" button.
- Solution:
@Asyncis used in theTopluBorclandirmaService.javaclass. While a "202 Accepted" response is returned to the user as soon as the request is received, the process continues in the background on a separate thread.
3.2. Financial Integrity and "Storno" Logic (Audit Trail)
An accounting record should never be physically deleted.
- Mechanism: In the cancellation method inside
FinansalIslemController.java, an erroneous transaction is not deleted (it is markedisCancelled=true). - Reverse Record: A "Correction Record" is automatically thrown into the system in the opposite direction (Expense if Income, Income if Expense) and in the same amount. In this way, the cash balance is mathematically corrected, but the transaction history is not lost.
3.3. Reporting with MongoDB Aggregation
Financial calculations made with standard loops (for-loop) are slow.
- Solution:
Aggregation Pipelineis used withinAidatKaydiRepository. - Technique: Instead of pulling data to the Java side and processing it, the calculation is done by the database engine (MongoDB) (
$group,$sum,$cond). This increases reporting speed by 10x-100x.
3.4. Extraordinary Expense Reflection
One of the system's "smartest" features.
- An "Expense" entered in cash movements (e.g., Elevator Maintenance) can be divided equally among all flats and reflected as "Debt" with a single click if desired (
BorclandirmaController).
4. Modules and Functionality
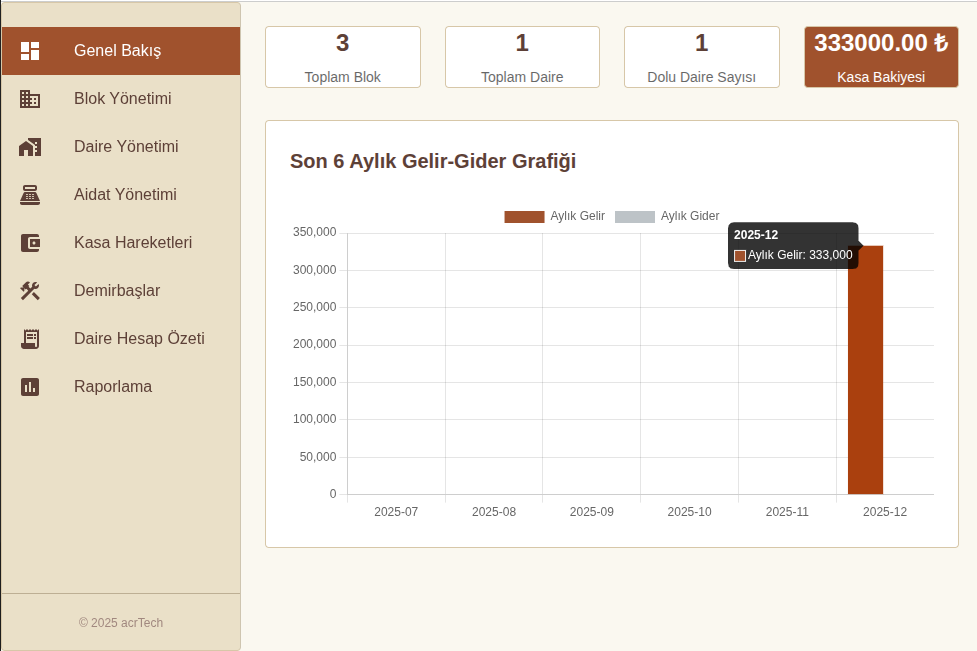
4.1. Dashboard and Overview
- The Income-Expense balance of the last 6 months is visualized with Chart.js integration.
- Instant cash balance and occupancy rates are presented in summary cards.
4.2. Flat and Block Management
- Flats are tracked under "Property Owner", "Tenant", or "Empty" statuses.
- Contact information and resident history are under record.
4.3. Fixture Management
- Physical assets of the site (Lawn mower, Generator, etc.) are tracked along with their status (In Use, Broken, In Service).
4.4. Cash and Current Account Tracking
- Income and expense items are categorized (Electricity, Water, Personnel).
- Receipt or invoice tracking is done in a digital environment.
5. Live Demo and Access
The live demo environment simulating the system's desktop experience via a web browser is active.
Demo Address: https://app-siteyonetim.acrtech.com.tr (Note: Changes made in the demo environment may be reset periodically.)
6. Conclusion
ACR Site Management System is not just simple software that collects dues; it is a modern ERP solution that applies accounting standards (Storno) in the background, optimizes database performance with Aggregation, and carries the user experience to the desktop with Electron.